
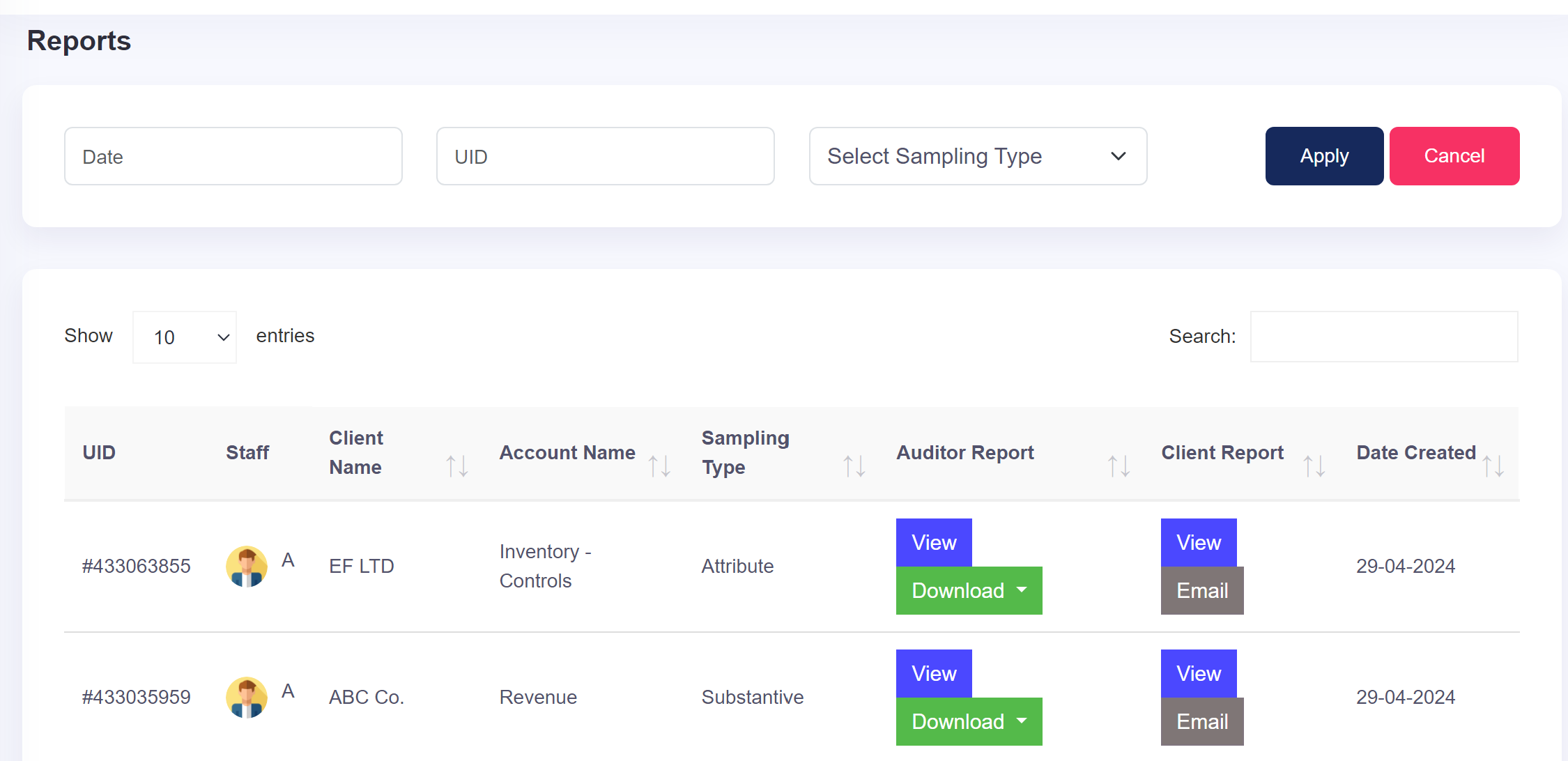
Dear Viewer,
In the ever-evolving landscape of auditing and financial oversight, the need for robust, efficient, and tamper-proof audit sampling processes has never been greater. At The Smart Sampler, we understand the challenges you face - from ensuring the integrity of your samples to maintaining compliance with rigorous standards such as those set by Generally Accepted Auditing Standards (GAAS) and International Standards on Auditing (ISA).
We are excited to introduce The Smart Sampler
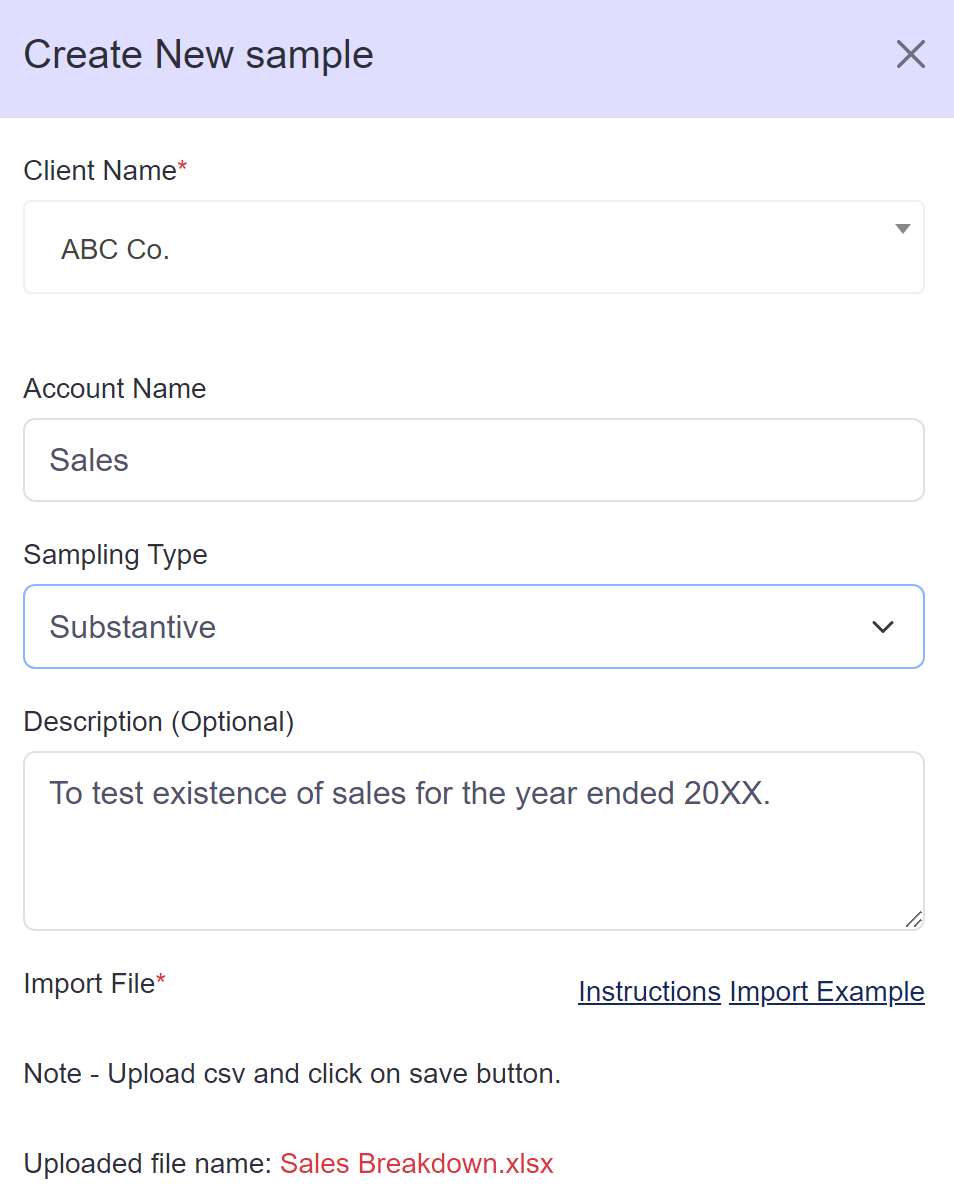
Choose a sampling type
Is a method used in auditing to test the presence or absence of certain qualities or attributes within a population, with the aim of drawing conclusions about the entire population. This type of sampling is typically used in tests of controls. Auditors use attribute sampling to determine whether the controls that an organization has put in place are operating effectively and whether they can be relied upon to prevent or detect errors in the financial statements.
Is a method used in auditing to test the presence or absence of certain qualities or attributes within a population, with the aim of drawing conclusions about the entire population. This type of sampling is typically used in tests of controls. Auditors use attribute sampling to determine whether the controls that an organization has put in place are operating effectively and whether they can be relied upon to prevent or detect errors in the financial statements.
Choose a plan as per your need
Questions Asked
For Attribute sampling, our tool offers two techniques: Random and Systematic. For Substantive Sampling, three techniques are available: Monetary Unit Sampling (MUS), Random, and Systematic. These options provide comprehensive coverage and flexibility to the user audit procedures.
Yes, users under the same company admin can verify samples in the tool. Every user signing up for the platform will have a company admin account, granting them the ability to manage user access within their organization. This includes adding and removing users as per their subscription plan. However, to verify samples, users will need to provide the UID number of the sample to access the relevant information. This ensures that only authorized users within the organization can access and verify samples, maintaining data security and confidentiality.
Is a method used in auditing to test the presence or absence of certain qualities or attributes within a population, with the aim of drawing conclusions about the entire population. This type of sampling is typically used in tests of controls. Auditors use attribute sampling to determine whether the controls that an organization has put in place are operating effectively and whether they can be relied upon to prevent or detect errors in the financial statements.
For example, an auditor might use attribute sampling to check if purchase orders over a certain amount have been approved as per the company's internal control procedures. The focus is on whether the attribute (approval) is present or not for each sampled item.
These definitions and examples are aligned with principles laid out in the International Standards on Auditing (ISA).
Substantive Sampling (or substantive testing) is used to evaluate the correctness of the balances and transactions in the financial statements. It involves direct verification of the amounts and other data through methods such as confirmation, inspection, and recalculation. Substantive sampling is used to gather evidence that the balances and transactions are free from material misstatement.
An example of substantive sampling would be selecting a sample of transactions from the sales ledger to verify that they are correctly recorded and supported by appropriate documentation (invoices, delivery notes, etc.), and accurately reflect the economic events that occurred during the period.
These definitions and examples are aligned with principles laid out in the International Standards on Auditing (ISA).